LABELLED ABSCISIC ACID
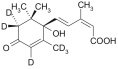
[2H6](+)-cis,trans-ABSCISIC ACID (2H-ABA) [(S)-5-[2H6](1-hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethyl-4-oxocyclohex-2-en-1-yl)-3-methyl-(2Z,4E)-pentadienoic acid]
| MW 270.36;
crystalline; purity > 98% (HPLC) |
|
CAS: 35671-08-0; C15H142H6O4 |
|
| 034
2721 |
1 |
mg |
| 034
2722 |
2
|
mg |
| 034
2723 |
5
|
mg |
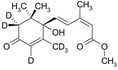
[2H6](+)-cis,trans-ABSCISIC ACID METHYL ESTER (2H-ABAMe) [(S)-5-[2H6](1-hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethyl-4-oxocyclohex-2-en-1-yl)-3-methyl-(2Z,4E)-pentadienoic acid methylester]
| MW 284.38;
crystalline; purity > 98% (HPLC) |
|
CAS: 35671-08-0; C16H162H6O4 |
|
| 034
2761 |
1 |
mg |
| 034
2762 |
2
|
mg |
| 034
2763 |
5
|
mg |