SYNTHETIC AUXINS
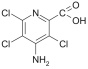
PICLORAM [4-amino-3,5,6-trichloropicolinic acid]
| MW 241.46;
crystalline; purity > 98% (HPLC) |
|
CAS: 1918-02-1; C6H3Cl3N2O2 |
|
| 016
2901 |
1 |
g |
| 016
2902 |
5 |
g |
| 016
2903 |
25 |
g |
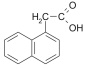
α-NAPHTALENEACETIC ACID (NAA)
| MW 186.21;
crystalline; purity > 98% (HPLC) |
|
CAS: 86-87-3; C12H10O2 |
|
| 016
2911 |
5 |
g |
| 016
2912 |
25 |
g |
| 016
2913 |
100 |
g |
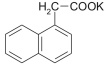
α-NAPHTALENEACETIC ACID POTASSIUM SALT (NAA-K)
|
MW 224.31; crystalline; purity >
90% (HPLC) |
|
CAS:
15165-79-4; C12H9KO2 |
|
|
016 6291 |
5 |
g |
| 016
6292 |
25 |
g |
| 016
6293 |
100 |
g |
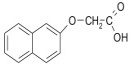
β-NAPHTHOXYACETIC ACID (BNOA)
| MW 202.21; crystalline; purity > 98% (HPLC) |
|
CAS: 120-23-0; C12H10O3 |
|
| 016
2921 |
1 |
g |
| 016
2922 |
5 |
g |
| 016
2923 |
25 |
g |
| 016
2924 |
100 |
g |
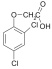
2,4-DICHLOROPHENOXYACETIC ACID (2,4-D)
| MW 221.04;
crystalline; purity > 97% (HPLC) |
|
CAS: 94-75-7; C8H6Cl2O3 |
|
| 016
2931 |
10 |
g |
| 016
2932 |
25 |
g |
| 016
2933 |
50 |
g |
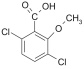
DICAMBA [2-methoxy-3,6-dichlorobenzoic acid]
| MW 221.04;
crystalline; purity > 97% (HPLC) |
|
CAS: 1918-00-9; C8H6Cl2O3 |
|
| 016
2951 |
50 |
mg |
| 016
2952 |
250 |
mg |
| 016
2953 |
1 |
g |
4-CHLOROPHENOXYACETIC ACID (4-CPA, CPA)
| MW 186.60;
crystalline; purity > 97% (HPLC) |
|
CAS: 122-88-3; C8H7ClO3 |

|
| 016
2961 |
10 |
g |
| 016
2962 |
25 |
g |
| 016
2963 |
100 |
g |